Research Computing Teams Link Roundup, 9 Oct 2020
Hi, all:
As I write this, the jurisdiction I live in (Ontario, Canada) is almost certainly about to start additional COVID-19 restrictions - 4-8 weeks later than it should have. The predictable, and predicted, second wave is reminding us that we're going to be dealing with the pandemic for some time to come.
This time has been hard for some of us, and extremely hard for others. I hope your team is doing well. I do think we will come out of this experience better managers - more deliberate about finding out our team members needs and in our communications, more thoughtful in our planning - but it's challenging and tiring, and I hope you take some time for yourself.
The roundup follows:
Managing Teams
It's Management, Not Micromanagement - Kristen Heyer, The Success League
Heyer pushes back on the fears that new managers often have of being "micromanaging":
Many newer managers confuse management with micromanagement. One of my favorite books on the topic of micromanagement (My Way or the Highway) defines it like this; “Micromanagement is when participation, collaboration and oversight interfere with performance, quality and efficiency.” Unfortunately, management (oversight that adds to performance, quality, and efficiency) often gets confused with micromanagement.
I agree - and I've seen way more undermanagement in research computing teams than I've seen micromanagement.
Heyer describes management approaches that are not micromanagement:
- Set metrics-based goals for your team.
- Hold weekly one-on-ones with all direct reports.
- Make performance and metrics transparent.
- Provide active coaching throughout their tenure, not just when they're onboarding
- Delegate tasks to team members who are ready
and has a nice table distinguishing micromanagement, management, and just not really managing:
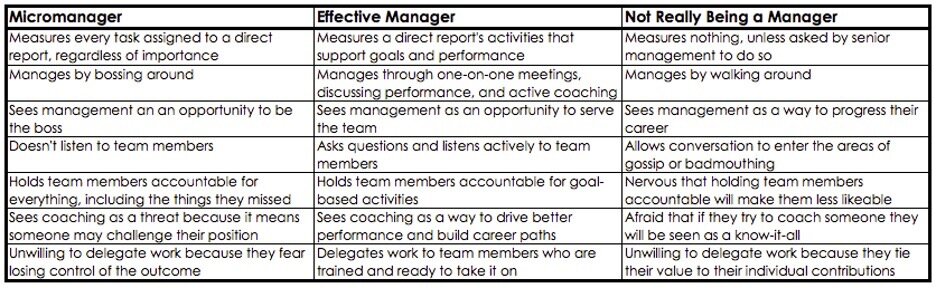
The way I like to think of it is that good management is holding your team members accountable to assigned tasks and goals at the right scope, the right level of detail, the level they've shown themselves routinely capable of handling. And that scope can and should expand over time. If you're inserting yourself into details that they have routinely demonstrated they're capable of handling without some good, clearly communicated reason, three bad things will happen. They're going to feel micromanaged, you'll be wasting your time, and you'll be risking losing that team member.
10 Habits That Help Me as a Manager - Marty Matheny
Matheny shares his habits he uses to stay focussed on the priorities, motivated, and fully charged:
Daily habits:
- Identify My Top Six Priorities
- Write and Share Daily Intentions (e.g. for standup - what is next for you)
- Keep an Emotional Journal (especially for stressful times like this if you find yourself reacting strongly to things)
Weekly Habits
- Update My Calendar - block off time for those priorities
- Exercise
- Review Indicator Metrics
- Record Impact I had
- Share a Weekly Update
Quarterly Habit
- Record My Quarterly Accomplishments
Annual Habit
- Create Personal OKRs
My own habits would look a bit like this - I tend to have priorities for a week, and tasks for a day (and try to keep my tasks focussed on my priorities as much as possible). How about you - what are the habits you have that keep you on track?
Help, I’m a Research Computing Manager! - Jonathan Dursi, SORSE event
At the really nicely run SORSE event last week, I gave my 10 minute pitch that research computing actually prepares you pretty well for the advanced skills managing needs, we just need to shore up the basics. The basics I covered won't be of a surprise to any readers - one-on-ones, feedback, delegation.
The talk and the resources I recommended are on the page; also, I updated my one-on-ones quickstart guide (PDF, epub) that had been written at the start of the pandemic to start them fast fast fast to instead start them up at a more normal pace.
The talk started with a poll - what are the problems the (mostly new or not-yet started) managers see in research software projects? Not surprisingly, they were almost overwhelmingly people or institutional issues:
| Fraction of respondents | Problem |
|---|---|
| 60% | Staffing |
| 50% | Funding |
| 47.5% | Shifting needs/unclear requirements |
| 42.5% | Poor communications with stakeholders |
| 30.0% | Getting poeple in agreement on howto move forward |
| 25.0% | Poor support from other departments/institutions |
| 17.5% | Technology choices |
Managing Your Own Career
How to Decline a Meeting - Another Task Done
There's no such thing as time management; managing time isn't a power given to we mere mortals. For us, there's only task management. And the first and most important task management skill is saying no to them.
This post give some helpful sample text for politely declining four kinds of meetings:
- The weekly status meeting that you don't have any real role in
- The meeting with no agenda - always a red flag
- The brainstorming meeting - at least cutting down the length of these
- The information broadcast meeting - shouldn't exist, but they do
One of the big challenges new managers face is that they finally get to be At The Table for stuff so they want to be at every meeting they get invited to. That's normal - how are you supposed to know what meetings are important for you and what aren't until you've gained some experience? As the novelty wears off you have to disentangle yourself from meetings, and these are a good way to start.
Product Management and Working with Research Communities
Research managers need friends in high places - Anne Katrin Werenskiold and Meike Dlaboha - subscription required
Unfortunately this article now needs a subscription to view, but it's interesting that following the success of RSE (research software engineers) in defining a role and ensuring institutional support, other research support professionals like research officers in Germany (this article) and Professional Research Investment and Strategy Managers (PRISMs) in the UK are advocating for more support, funding, and career ladders for their roles.
Research Software Development
How to make research software a first-class citizen in the Netherlands? - NL-RSE
Raising the Profile of Research Software: Recommendations for Funding Agencies and Research Institutions in the Netherlands - Akhmerov, Anton; Cruz, Maria; Drost, Niels; Hof, Cees; Knapen, Tomas; Kuzak, Mateusz; Martinez-Ortiz, Carlos; Turkyilmaz-van der Velden, Yasemin; and van Werkhoven, Ben
As more of these white papers come out it's interesting to see the commonalities and differences between them. In the blog post, NL-RSE emphasizes the contributions of Leeuwenhoek, who could not have done his pioneering microbiology work without having also made high quality tools - his lenses.
The quite short white paper makes and justifies very specific recommendations, which I've paraphrased for length:
Software availability and quality
- Require that software generated as part of research is archived in compliance with the FAIR principles
- Open-source research software development by default
- Provide full lifecycle support for storing and sharing software, including archiving
- Encourage best practices in software development
Software sustainability
- Fund open-source software development important to academic research for full life cycle
- Stimulate community building and workshops around important software topics
- Survey the research software community to identify the needs for maintaining specific software packages.
- Require grant proposals to make a strong case for specific existing software to be used in the proposed research project.
- For grant proposals where new software is proposed to be developed, explain why the existing software is not sufficient either for use or collaborative development
Training
- Include algorithmic thinking and data management in all core curricula of academic institutions at both undergraduate and graduate level.
- Provide training opportunities for researchers to develop digital skills
- Provide researchers with support and guidance on digital competency.
- Stimulate the training of specialists on digital competency skills (Research Software Engineers and Data Stewards).
Human capital
- Formalize of Research Software Engineer (RSE) and Data Steward roles, with career progression paths.
- Recognize and reward all research outputs
Dual licensing GPL for fame and profit - George
I'm a big fan of copyleft licenses for research computing projects (though I don't always win these arguments at work). I understand the arguments in favour "freer" licenses. and they have their place, but copyleft seems extremely consistent with academic approaches to credit. More to the point it's not an either/or thing; there's no reason why code can't be dual licensed, available as GPL for free for those to whom it meets their needs, and at some charge under other licenses for those who want to be able to distributed change versions of the code without making those changes public.
I'm not naive enough to think this is a sustainability model for much or any of research software, but it's odd to me that it's so rarely even discussed as an option. This blog post lays out how it works and some of the benefits.
These are two interesting packages for making it easier to recognize contributors to open source repositories. It looks like All Contributors is a github bot which you can give commands to and will make PRs to a list of files (such as README) to include contributors; Tributors updates some of the standard code metadata files we read about in issue #44 using Github actions.
Translate your data with lenses - Geoffrey Litt, Peter van Hardenberg, Orion Henry
This is a kind of tool I've been looking for examples of for some time. It's a DSL to implement mappers from one schema to another. They use mapping between ticket trackers, API versions, and Kafka events as examples. This is such a common task in data munging and there's so much boilerplates involved that it's a wonder there aren't more tools like this. Does anyone use anything similar?
Research Computing Systems
The How (and Why) of User Flows - Learn UXD
This is a good short introduction to how to plan or document user flows. The context of the article is doing it for web or mobile applications, but really it can be applied to any process a user has to go through (often then called "service design").
I'm putting this in "Research Computing Systems" because I think in research software development or data management, the research computing teams are generally pretty decent at imagining themselves as the users - writers of simulation or data analysis software for research are often using the software themselves or working very closely with the people who are.
On the other hand the operators of research computing systems are more often - not universally, but more often - quite detached from the day-to-day users of the systems. As a result, for instance I've seen user registration processes which are complicated messes which make perfect sense when viewed from the inside as each step ticks some box but from from the outside is convoluted and opaque. Stepping through the user flows helps visualize things from the user's point of view and points out steps that can be simplified or consolidated.
On Call Shouldn't Suck: A Guide for Managers - Charity Majors
Speaking of imagining things from another's point of view, Majors points out that if we're going to make people be on call for our systems, we owe it to our whole team to put in the effort elsewhere to make sure the on-call experience is reasonable - avoiding tech debt, lots of testing, etc. The context is applications but the same is true of the computing systems themselves:
It is easier to keep yourself from falling into an operational pit of doom than it is to claw your way out of one. Make good operational hygiene a priority from the start
The most controversial recommendation is that you should be able to operate in a mode where on-call is voluntary, and if you can't there's some other underlying problems.
The second most controversial recommendation from our point of view is that managers should be chipping in, at least as backups :)
Applying Chaos Engineering in Healthcare: Getting Started with Sensitive Workloads - Carl Chesser, writing at InfoQ
I've heard more than once when talking about some version of chaos engineering - intentionally failing processes and nodes to make sure the computing system as a whole is resilient - that "we can't do that in research computing environments, researchers depend on us!"
Well, here's what they do at Cerner corporation, which makes and runs hospital information systems like health records. Chesser is a principal engineer there and describes how to get started with critical systems like HIS. As always, a deliberate approach towards improved professional practice is the way to go:
With critical systems, it can be a good idea to first run experiments in your dev/test type environments to minimize both actual and perceived risk. As you learn new things from these early experiments, you can explain to stakeholders that production is a larger and more complex environment which would further benefit from this practice.
Emerging Data & Infrastructure Tools
Unlocking eBPF Power - Michał Wcisło
How eBPF Turns Linux into a Programmable Kernel - Joab Jackson, The New Stack
eBPF, started off as Berkeley Packet Filters - allowing processing and monitoring of packets. It now is essentially a way to run almost-arbitrary functions in sandboxed kernel space (stored procedures for the kernel). These two recent articles explore eBPF's capabilities.
Wcisło's article is very hands-on, and he walks the reader through his path - starting from nothing, not even knowing how to start, through a solution with code samples, of locking and suspending is laptop using his phone's Bluetooth.
Jackson's New Stack article covers a technical session at KubeCon + CloudNativeCon EU, and a series of talks (with linked video) on how eBPF is being used for observability into or helper functions for Kubernetes, and a talk on tooling to make it easier to write eBPF code.
OpenHPC 2.0 - HPCWire
OpenHPC 2.0, the software stack for HPC clusters, is out. This isn't intended to be backwards compatible with the 1.x series, and it's intended for people who are starting with a new system. I love the idea of a "standard distro" for HPC clusters; is anyone actually using this?
Events: Conferences, Training
How to understand and improve the performance of your parallel applications using the POP Methodology - Fouzhan Hosseini, SORSE event, Oct 16 09:00 – 09:30 UTC
Becoming a self-employed RSE web developer - Dr. Teri Forey, SORSE event, Oct 16 09:30 – 10:00 UTC
Next up in the SORSE series - parallel performance and freelancing. The talks and Q&A are recorded and show up after a week or so on the SORSE youtube channel.
Persistent Programming In Real Life (PIRL) - Fridays Oct 16, 23, 30 - $50 USD
Tools, approaches, and lessons learned from programming with persistent memory (Intel Octane and the like).
Random
A paean to nethack.
You can get a properly shell-quoted string by typing in the string as a comment in one line on the terminal and then using a history expansion - !:q.
Interesting looking book on applied cryptography, probably at the right level for research computing, coming as a Manning MEAP. Also an interesting approach for a book - starting with the diagrams (drawn for talks, training etc).
argbash - a bash code generator for command-line argument handling.
Not entirely sure what to think about NVIDIA's DOCA system - what are people's impressions? It may enable some cool things.
T-SQL compiled stored queries.. for sqlite. (I love embedded databases, so any cute new duckdb/sqlite/leveldb/whatever article or tool will always find its way into the newsletter)
A really nice interactive git tutorial.
Relatedly - the (wrong, but interesting) argument against squashing commits.
Relatedly again - the (wrong, but interesting) argument for just always merging into the main branch.
Manubot: an all-in-one setup for writing your manuscript in markdown with git and publishing into PDF, HTML, or docx with Github actions (or, less feature-fully, Travis-CI).
It's not news when a climate/weather centre gets a new cluster, or that they're playing with machine learning. It becomes news when they're also partnering with the vendor to play with quantum computing applications.
Getting experience with IPv6 by setting up your home IPv6 network.
That’s it…
And that’s it for another week. Let me know what you thought, or if you have anything you’d like to share about the newsletter or management. Just email me or reply to this newsletter if you get it in your inbox.
Have a great weekend, and good luck in the coming week with your research computing team,
Jonathan
Jobs Leading Research Computing Teams
Highlights below; full listing available on the job board.
Research Associate - Bioinformatics - BC Genome Sciences Centre, Vancouver BC CA
The GSC is currently looking for a senior bioinformatician to develop approaches to analyzing and sharing “big data”. This role is instrumental in the development of the CFI-funded cyberinfrastructure project, CanDIG—a state-of-the-art data sharing platform contributing to the development of an international effort to facilitate information exchange as part of the Global Alliance for Genomics & Health (GA4GH). CanDIG also supports large-scale provincial and national data sharing projects, including BC Cancer’s Personalized OncoGenomics program, the Terry Fox Research Institute (TFRI) PROFYLE project and the TFRI-led Marathon of Hope Cancer Centres Network—a major federal initiative to accelerate the adoption of precision medicine for cancer in Canada.
HPRU Database Manager - Imperial College London, London UK
The postholder will lead data curation and mobilisation within the NIHR HPRU in Respiratory Infections, a flagship partnership with Public Health England (PHE) conducting state of the art research to support public health services. Our continuing goal is to protect and improve the public’s health through better application of cost-effective public health interventions. Funded by the HPRU is the hub of an integrated consortium comprising world-class expertise in all areas of laboratory, public health, epidemiology and health-economic sciences.
Head of Data Engineering and Science - Just Retirement, London or remote UK
The role will focus on our move from a data integration and operations approach, based on standard ETL methods, to planning and executing an integrated multi-year data engineering and data science strategy; developing and driving our engineering stack through containerization, data frameworks/modelling, developing our data pipelines, data optimization, artificial intelligence, machine & deep learning, and search, natural language processing and analytics.
Group Manager, Automation and Research Computing - Federal Reserve Board, Washington DC USA
The Group Manager (GM) role in Automation and Research Computing (ARC) section reports to the ARC Chief and is responsible for managing a technical team of staff. At the direction of the ARC Chief and with guidance from division officers, the GM works with staff to operationalize and implement Research technology programs and services. The section develops and operates a dynamic computing environment optimized for economic research, analysis, and measurement, and made available to staff across the Board's economics divisions. As a member of the ARC leadership team, the GM works closely with the Chief and other managers and staff to implement both strategic and tactical goals, fosters innovation, develops talent, and directs work.
HPC Systems and Data Engineer - San Diego Supercomputing Center, San Diego CA USA
The incumbent will apply skills as a seasoned, experienced systems integration professional with a full understanding of systems and software integration concepts to evaluate, resolve and implement medium-sized projects or portions of large projects with moderate scope and complexity. S/he will resolve a wide range of business processes, system functionality, implementation issues and system and software integration issues. The incumbent will need to demonstrate competency in selecting tools, methods and techniques to obtain results, give technical presentations to associated teams and other technical units, and evaluate new technologies including performing moderate to complex cost/benefit analyses. S/he may lead a team of systems/infrastructure professionals.
Chief Technology Officer - Health Data Research UK, London UK
This is a high-profile leadership role with major UK-wide responsibilities and so it is essential that you have authoritative knowledge and understanding of enterprise architecture concepts, agile system development and open source. You will be capable of building effective relationships and networks of individuals and organisations, both within the UK and internationally, with proven business analysis and leadership skills.
Project Manager - Multilearning, Work from home CA
MULTILEARNING is a provider of Hybrid Virtual Event & eLearning platforms, tools, and solutions for scientific organizations worldwide and has celebrated its 20th anniversary this year.
Evaluate, discuss and prepare Projects with colleagues and clients located worldwide
Set and respect communication flows with clients during the whole project
Assist clients in the integration of educational content, including making suggestions based on best practices (user experience, instructional design)
Collaborate with the development team on validation of new features (web/mobile)
Senior Advanced Research Computing Analyst - University of Victoria, Victoria BC CA
Reporting to the Manager, Research Computing Services, the senior advanced research computing specialist works as part of a team to assist researchers with their data science and research computing needs and questions. Members of this team offer critical support to many research groups on-campus, including training researchers to use local, regional, and national advanced research computing (ARC) systems such as HPC clusters, clouds, and bigdata platforms, debugging their codes, suggesting ways to improve the performance of their jobs and programs, helping them choose the most suitable ARC system for their computational requirements and workloads, and directing them towards the best data science tool and technology to solve their research questions.